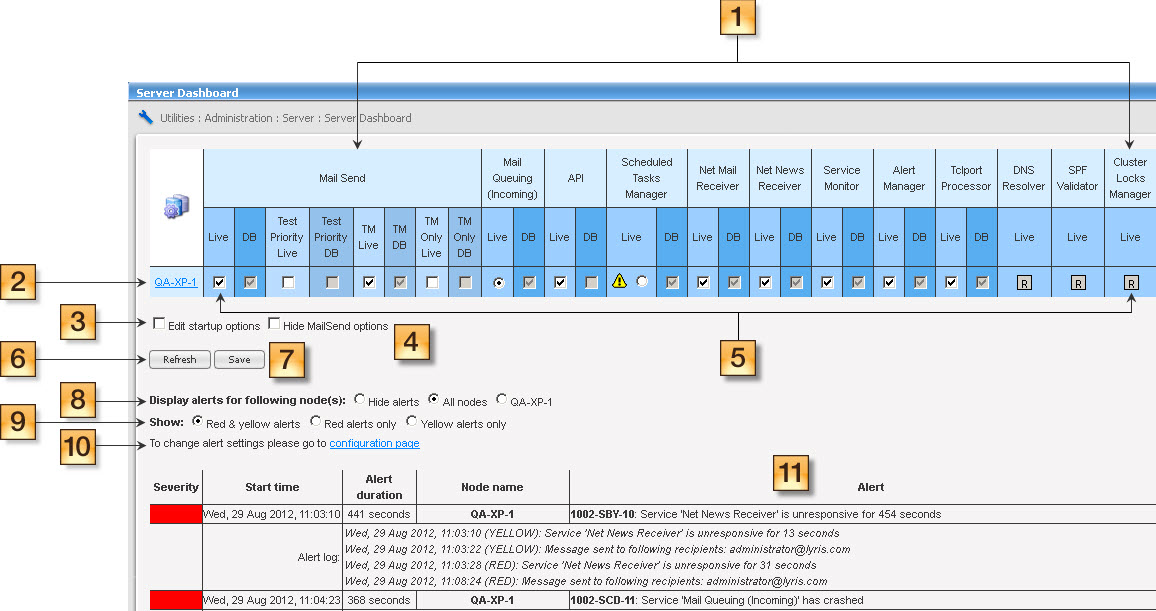
The Server Dashboard gives you the ability to monitor and configure a server and individual nodes in a clustered server.
TIP: For more information about nodes and clusters, see Clustering ListManager.
The Server Dashboard shows all nodes and services, the status of each one, and the alerts that help you identify potential problems.

 List of all services
List of all services
The Live column for each service shows the current state of the service. Services that must always be running on every node, such as DNS Resolver, show only the Live column. Services that you can turn on/off show an additional column, DB. The DB column specifies the service startup option. For example, in the illustration above, the API DB checkbox in not selected. This means that the API service will not run when the server starts.
If a service has multiple options that you can turn on/off individually, such as the Mail Send service, the Server Dashboard shows a Live and DB column for each option, for example Test Priority.
 List of all nodes
List of all nodes
Click the name of a node to see all services and the current state of each service. For more information, see Utilities: Debug Facilities: Services.
TIP: For more information about nodes, see Clustering ListManager.
 Edit startup options
Edit startup options
Select this checkbox to specify the service startup options. When you select this option, you can edit the settings in the DB column.
 Hide MailSend options
Hide MailSend options
Select this checkbox to hide the Test Priority and TM columns of the Mail Send service. You might want to do this to save screen space.
 Status of all services
Status of all services
Indicates the status of the service:
 —the service is running.
—the service is running.
 —in the Live column, indicates that the service is not running. In the DB column, indicates that the service will run when the server starts.
—in the Live column, indicates that the service is not running. In the DB column, indicates that the service will run when the server starts.
 —applies to services that can run on only one node. Indicates that the service is activated on the node.
—applies to services that can run on only one node. Indicates that the service is activated on the node.
 —applies to services that must always be running on every node. Click this button to restart the service.
—applies to services that must always be running on every node. Click this button to restart the service.
![]() —a warning. Point at this icon to see the warning message.
—a warning. Point at this icon to see the warning message.
 Refresh
Refresh
Click this button to update the Server Dashboard.
 Save
Save
Click this button to save your settings.
 Display alerts for following node(s)
Display alerts for following node(s)
Specifies the nodes for which to display alerts:
Hide Alerts—does not show alerts for any nodes.
All nodes—shows alerts for all nodes.
<Node name>—shows alerts only for the selected nodes.
 Show alerts
Show alerts
The types of alerts to show: red and yellow, only red, or only yellow.
To show alerts, you must enable them on the Utilities: Administration: Server: Server Settings: Alert Settings page.
 Link to Alert Settings page
Link to Alert Settings page
Gives you the ability to change the server alert settings. For information about setting alerts, see Utilities: Administration: Server: Server Settings: Alert Settings.
 Alert log
Alert log
Shows the history of alerts that the server creates when resource levels exceed your configured thresholds.
To show alerts, you must enable them on the Utilities: Administration: Server: Server Settings: Alert Settings page.
Severity—the severity of the alert, green, yellow or red
Green alerts indicate that a yellow or red alert has been corrected and does not exist anymore. Yellow alerts indicate a warning. Red alerts indicate a potentially critical server condition that might required action.Start time—the time when the alert was raised
Alert duration—the length of time that the condition has existed
Node name—the name of the node where the condition exists
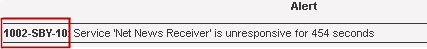
Alert—the description of the condition
In addition to the description, the Alert column shows the alert id in the following format:<Node ID>-<Condition Code>-<Alert Number>
The condition codes are:
SDN—ServiceDown. A service should be running but has exited prematurely.
SBY—ServiceBusy. A service is running but has been unavailable for longer than the threshold time.
SCD—ServiceCrashed. Available only on Windows. A service has exited abnormally (crashed).
SDD—ServiceDowngraded. Available only on Windows. A service is running and available, but has lost some of its service threads. This condition indicates that the service might be in imminent danger of going down.
DBC—DBConnection. Database connection usage has risen to the threshold values.
LRQ—LongRunningQuery. A SQL query is taking longer to execute than the threshold time. Long-running queries can impede other server activity.