DKIM/DomainKeys FAQ
The frequently asked questions below provide you with a good foundation for working with DKIM. To go directly to the topic that explains how to set up and use DKIM/DomainKeys in ListManager, click here.
What is email authentication?
Email authentication is a way to ensure that email actually comes from whoever it claims to come from. It's a vital step in stopping spam, forgery, fraud, and even more serious crimes.
What is DKIM?
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is a secure method for associating a domain name with an email message. The association is setup by the means of a digital signature which can be validated by the recipients. Responsibility is claimed by the signer ‑ independently of the message's actual authors or recipients. DKIM is the result of merging DomainKeys and Identified Internet Mail.
DKIM stands for "DomainKeys Identified Mail." It is an enhanced version of DomainKeys. (Learn more about the differences.)
DKIM uses something called a digital signature.
What is that?
DKIM allows senders to associate a domain name with an email message, thus vouching for it's authenticity. This is done by signing the email with a digital signature, which is a technology used to simulate the security properties of a handwritten signature in digital form. This is accomplished by creating a "private key," available on your outbound mail servers, and a matching "public key," which you publish in DNS. When you send email, your email system automatically uses the stored private key to generate a digital signature of the message which is then attached to the message. The receiving email system fetches the public key from DNS and uses it to verify that the signature was generated by the matching private key (or not).
How does DKIM help with branding?
Preventing forged email helps you in a number of ways, including branding. Using DKIM reduces the chance that someone will impersonate your domain and use it for fraudulent purposes, including "phishing attacks" -- the solicitation of personal information such as passwords, credit card numbers, etc.
How does DKIM help with deliverability?
Using DKIM doesn't guarantee that your email will bypass any spam filters on the receiving end, but if your recipients can confirm that the email truly came from you, and if they consider you someone of good reputation, they are more likely to receive and open your mail.
What are email "headers"?
Headers are pieces of information that get attached to email as it makes its journey from the sender, through various computers on the Internet, and on to the receiver. Here is an email that was sent from Yahoo; some of the more basic headers are outlined, including:
Date: the date the email was created.
From: who sent the email (supposedly).
To: who it's going to.
Subject: the subject line created by the originator of the email.

Why are headers important to DKIM?
When you use DKIM, a header called DomainKey-Signature: is added to each email. This header contains the digital signature of the message which was generated using the stored private key described in the above section about digital signatures. You can learn more about it here.
What is the difference between the "From"
header and the "Sender" header?
The From header contains the creator(s) of the message; the Sender header contains the mailbox of the agent responsible for the actual transmission of the message. In many instances, these are one and the same, in which case only the From header is used. There may be situations where these are two separate entities; for example, if a secretary were to send a message for another person, the mailbox of the secretary would be in the Sender header and the mailbox of the author(s) would appear in the From header. If there are two or more authors (and therefore two or more From mailboxes), the Sender header, with a single mailbox listed, must appear in the message.
How is this information about the From and Sender headers
useful when using ListManager?
If the ListManager Internet Host Name domain of the site and the From domain match, ListManager includes the From header but not the Sender header in the digital signature. If the ListManager site name and the From domain are different, the Sender header is included.
I sent some mail and then viewed it in Outlook. In the
From field, it said "From <address 1> on behalf of <address
2>." Since the email looks like it came from two different places, I'm
concerned that recipients will view it suspiciously. What's going on?
This occurs in Outlook if you have a From header and a Sender header. Outlook interprets this as "From <Sender header> on behalf of <From header>."
If you are concerned about what your Outlook recipients will see, ensure that your outgoing mail only contains a From header, not a Sender header.
How can I ensure that my email only has a From header?
One solution would be to use an autoresponder. You can learn more about autoresponders here.
You can also choose a list level setting for DomainKeys that prevents use of a Sender header.
I sent a message and then opened it in Yahoo and looked
at the headers. I'm pretty sure there should be a Sender header, but none is
displayed. Why?
Yahoo does not display the Sender header, even when you view all headers.
How can I test DKIM?
Send a message to any Yahoo address and then view the headers.
Does Yahoo require DomainKeys for its Feedback Loop?
Yes. Contact your Yahoo representative for Feedback Loop applications.
When I open a typical email, I only see a few of the most
basic headers. How do I view all headers in Yahoo / Outlook / Gmail?
In Yahoo:
1. Open the email.
2. Click on Actions in the toolbar.
3. Select View Full Header to see the complete email header content.

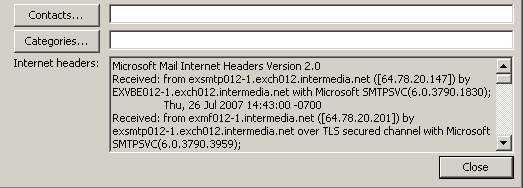
In Outlook:
1. Open the email.
2. In an open message, click the File tab.
3. Click Properties.
In Gmail:
1. Open the email.
2. At the top-right of the message pane, click the down arrow next to Reply.
3. Select Show Original.

What happens if I send a mailing for which DKIM has been set up incorrectly?
See the topic "Failed Verifications and Warning Messages."
The From: field in my mailing contains a merge tag. Will DKIM still validate it?
No; ListManager will not merge and then validate the domain. The mailing will be signed and sent out, but you must verify that the domains match.
Note: Before you turn on DKIM, make sure that DKIM verifies correctly.
Next: Setting Up and Using DomainKeys in ListManager